Entrepreneurs who own a trademark, copyright, or patent on an item or technology enjoy an edge over their competitors. Regardless, the cycle to achieve this intellectual property protection can be long and confusing. Before you start the cycle, it’s important to find out the differences between a trademark, copyright, and patent We’ll walk you through how each can help protect your organization’s intellectual property, what exactly they protect, and where you can apply.
Purpose amp Play is an annual design competition and exhibition that explores new prototypes for contemporary life focusing on domestic objects that are fun to use and fun to own It showcases new work from seven Canadian designers and studios View the exhibition live at the Umbra Concept Store, Jan 16 through Feb. Click Now.
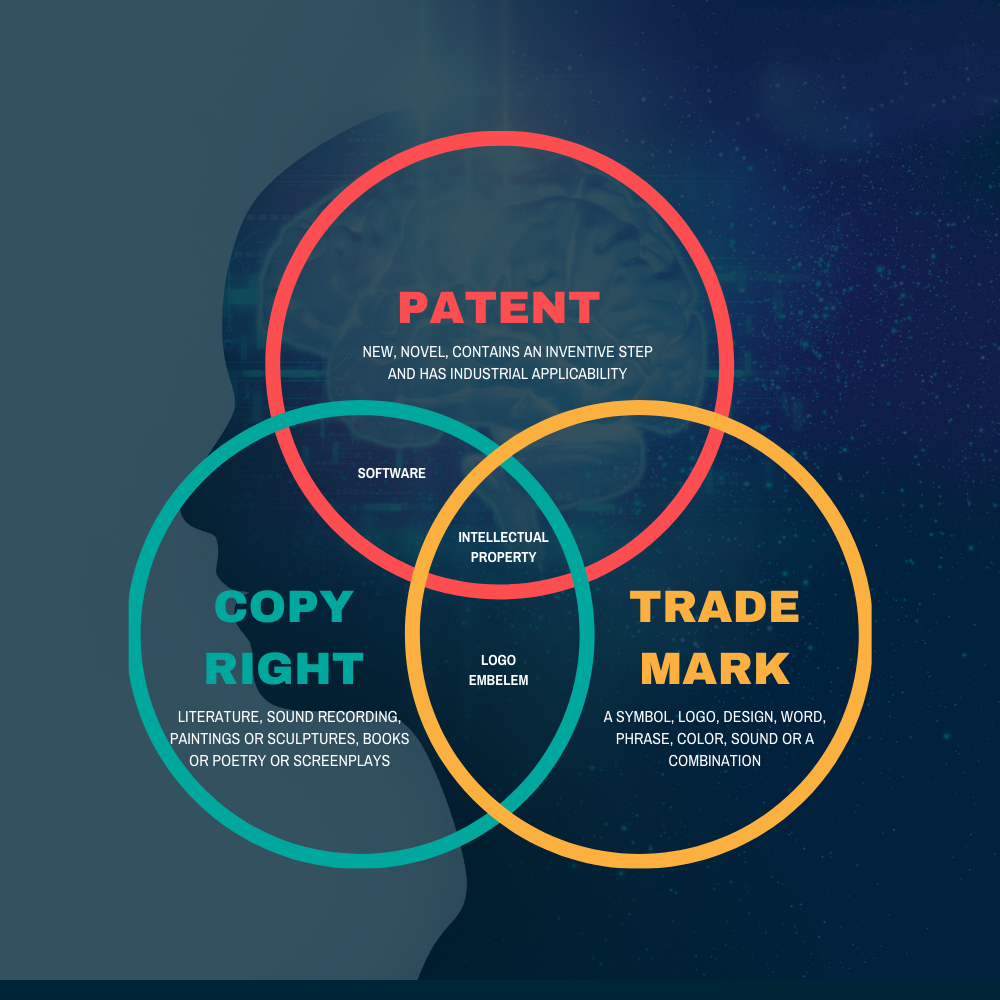
Definition of Copyright, Trademark, and Patent
Copyrights are registered by the US Copyright Office at the Library of Congress while the US Patent and Trademark Office grants patent and trademark registrations.
Here is a brief explanation of each type of intellectual property.
trademark
A trademark can be a phrase, word or design that distinguishes your organization and its labor and products. A trademark can help distinguish you from your competitors and prevent others from using your impression. There are state-level and government-level trademarks, each with its own registration cycle.
patent
A patent is a recognized property of the creator(s) of a new, exceptional and helpful invention, disclosure, or interaction. Patents allow you to exclude others from making, using or selling your invention. There are three main types of patents: utility, design, and plant.
copyright
Original works of copyright-protected authors including songs, books, moving pictures, articles, and significantly more. The key is that the work must be in a physical or computerized medium such as paper, film, or a computerized document. A copyright gives you the exclusive right to incorporate the work in several ways: you can imitate it, sell or distribute copies, show it, perform it, or do other things based on your copyrighted work. Copyrights are automatic upon creation of the original work, however, registration is advised so copyright claims are essential for openly available reports.
Purpose amp Play is an annual design competition and exhibition that explores new prototypes for contemporary life focusing on domestic objects that are fun to use and fun to own It showcases new work from seven Canadian designers and studios View the exhibition live at the Umbra Concept Store, Jan 16 through Feb. Click Now.
Benefits of obtaining copyright
Copyright is recognized the second you create an original work in an exact or fixed form. It’s automatic. However, unregistered works can be challenging to demonstrate in the event that someone else uses or takes your work. Additionally, you can only record a copyright claim on the off chance that your copyright is listed. This is why we recommend registering your work with the US Copyright Office to make a publicly available report of your copyright claim.
Benefits of getting a government trademark
Having a trademark means that your competitors cannot register a very similar, or a confusingly comparable, trademark in the same class of labor and goods for which your trademark is registered. Registration creates an openly available record of your trademark ownership and allows you to use the ® image, convey authenticity and deliver it to your customers and avoid counterfeiting. Likewise, an official trademark gives you additional means of enforcing the imprint and prepares you to register your imprint in other countries.
Benefits of having a patent backed
Innovations can take a long time to develop and are often expensive. Obtaining a patent guarantees that you will have the opportunity to profit from your continued efforts. In a patented system, the invention and any associated circuits cannot be copied, manufactured, or sold without permission from the inventor.
Copyright vs Trademark vs Patent
US government law covers intellectual property, an opportunity that can be difficult to understand if you’re not a lawyer. Each type of intellectual property has different laws and requirements, so there are some basic concepts to understand before proceeding with your patent, copyright, or trademark.
Copyright protects original works, such as crafts, writings, or other created works.
A trademark protects the name, short motto, or logo.
A patent protects new inventions, cycles, and compositions of matter (such as drugs). Importantly, ideas cannot be patented – your invention must be typified in a cycle, a machine, or an item.
Purpose amp Play is an annual design competition and exhibition that explores new prototypes for contemporary life focusing on domestic objects that are fun to use and fun to own It showcases new work from seven Canadian designers and studios View the exhibition live at the Umbra Concept Store, Jan 16 through Feb. Click Now.
Conclusion
The decision to seek a patent, trademark or copyright relies upon the type of intellectual property you’re attempting to safeguard. Whether it’s another item, logo, or innovative work, enrolling your thought with the fitting body can assist with guaranteeing you partake in your rewards for all the hard work.
Important Affiliate Disclosure
We at https://patentomatics.com/ are esteemed to be a major affiliate for some of these products. Therefore, if you click any of these product links to buy a subscription, we earn a commission. However, you do not pay a higher amount for this. Rest easy as the information provided here is accurate and dependable.